Last Updated on April 9, 2025 by Admin
Highway engineering remains an integral discipline in constructing and developing modern transportation networks. With rapid technological advancements, population growth, and the push for sustainable solutions, highway engineers are in higher demand than ever. This post will cover the highway engineer’s job description, key duties, education requirements, salary ranges, career paths, industry trends for 2025, and more.
ConstructionCareerHub App is LIVE — built ONLY for construction careers. Don’t apply with a weak resume.
Get ATS-ready Resume Lab + Interview Copilot + Campus Placement Prep (resume screening, skill gaps, interview readiness) — in minutes & Other advanced features.
Explore Smarter Construction Career Tools →Quick check. Big impact. Start now.
Table of Contents
Who is a Highway Engineer
Highway engineers are specialized civil engineers responsible for planning, designing, constructing, and maintaining roads, highways, bridges, and related infrastructure. Their work ensures safe, efficient traffic flow and connects people and goods across cities, states, and countries. A highway engineer might also design intersections, manage drainage and stormwater systems, and collaborate with environmental planners to minimize the ecological impacts of new roads.

A highway engineer’s job is to design and oversee the construction of roads, bridges, tunnels, and big parking lots. They are primarily concerned with roadway alignment, traffic control devices, drainage facilities, lighting, and pavement markings.
A typical day at work will include designing plans for new roads or modifying existing routes. Engineers must also calculate costs for these projects by surveying current traffic patterns.
There are three significant highway branches of engineering: planning, research, and construction. Most highway engineers specialize in one of these areas.
Planning engineers work with the city and regional planners. They try to figure out ways to reduce traffic congestion in congested areas. They analyze traffic patterns and keep current on constructing new buildings that might cause future traffic problems.
Highway engineers must also consider the impact of new roads on the environment. These workers are usually employed by the city, state, and federal governments and by consulting firms used by government agencies.
Highway planners may also work for transportation departments that control the transit systems of large cities.
Key Responsibilities at a Glance
- Designing and analyzing highway layouts
- Overseeing construction teams, budgets, and schedules
- Drafting project proposals and estimates
- Managing drainage, lighting, and traffic control systems
- Collaborating with government bodies, stakeholders, and planning committees
- Applying sustainability principles to modern transportation needs
What is Highway Engineering?
Highway engineering focuses on planning, designing, constructing, and operating roads and highways. It requires a strong understanding of traffic flow, drainage, geometric design, pavement materials, and environmental factors. Highway engineers ensure that road designs balance safety, efficiency, and cost while minimizing adverse environmental impacts.
Core Areas of Highway Engineering
- Planning – Identifying the best routes for new roads, addressing traffic congestion, and forecasting future travel needs.
- Research – Studying material properties, traffic patterns, and emerging technologies to improve road design and construction methods.
- Construction – Overseeing the building process, ensuring work meets standards, and managing budgets, timelines, and safety protocols.
Duties and Responsibilities of a Highway Engineer
The day-to-day tasks of a highway engineer can vary considerably depending on the scope of the project but typically include:
- Planning & Feasibility Studies: Conduct site surveys, analyze traffic data, and evaluate environmental impacts before drafting the initial design.
- Cost Estimation & Budgeting: Project financial requirements and manage resources effectively to stay within allocated budgets.
- Design & Engineering Analysis: Use specialized software like AutoCAD, Civil 3D, MicroStation, InRoads, or OpenRoads to develop accurate highway and roadway plans.
- Project Management: Coordinate with multidisciplinary teams, schedule tasks, and monitor project milestones to ensure timely and efficient completion.
- Compliance & Safety: Ensure designs comply with local, state, or federal standards. Incorporate safety features—signage, guardrails, and traffic lights—into roadway design.
- Collaboration & Reporting: Communicate with clients, contractors, government agencies, environmental planners, and the public to keep all stakeholders informed and involved.
Additional Responsibilities for Future-Focused Projects
With the rapid rise of smart technologies and sustainability requirements, highway engineers are increasingly involved in:
- Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS): Incorporating sensors, IoT devices, and real-time data collection to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion.
- Sustainable Materials & Practices: Using recycled materials, permeable pavements, and green infrastructure to reduce environmental impact.
- Resilient Road Design: Planning for extreme weather events, such as floods or heat waves, to minimize damage and service interruptions.
The role of a highway engineer is to oversee the costing, estimating, planning, and implementation of a project. This makes highway engineering a diverse and rewarding career, with day-to-day duties ranging from undertaking site surveys to preparing design specifications, organizing deliverable packages, etc.
You must have excellent leadership, communication, civil engineering, and highway engineering skills, with a drive to deliver infrastructure that will make safe, sustainable, healthy travel the natural first choice for people to move around our urban areas. The following are some of the deliverables for highway engineers.
- Support lead engineer to deliver roadway/highway design projects,
- Design of roadways and highways to meet local, state, and federal requirements,
- Analysis and design of different highway components,
- Maintain records of all design calculations,
- Direct CAD team to prepare highway drawings,
- MicroStation, InRoads, or OpenRoads experience preferred.
You will know about current highway design principles, construction standards, and highway contracts. You will have experience working in or with local government, stakeholder engagement, public consultation, and the management of teams delivering sustainable transport, highways, and road safety schemes.
The highway engineer job will involve liaising with other transport professionals around the globe, with some of the most significant projects taking place across the United States, Europe, Canada, and India.
How to become a highway engineer
How do I become a road engineer? A highway engineer job is a road to a rewarding career working on multi-disciplinary engineering projects.
Enroll for the bachelor’s or master’s degree program in Engineering and find opportunities to work alongside talented professionals, develop expertise, and gain exposure to an exciting range of projects.
Responsibilities include overseeing the personnel working on the project and preparing job budgets and schedules.
A highway engineer’s CV will show evidence of technical writing, computing, and communication skills and often experience using computer software such as AutoCAD and OpenRoads.
Over time, as these skills are honed, there is the option to progress to a senior highway engineer.
Education Qualifications and Experience Required
- Bachelor’s Degree: Typically in Civil Engineering, Highway Engineering, or Transportation Engineering.
- Master’s Degree (Optional but Beneficial): Specialized graduate programs in Highway/Transportation Engineering enhance career opportunities.
- Licensure & Certification: You may need a Professional Engineer (PE) license depending on your region. Certifications like the Highway Construction Inspection Certification can also boost credibility.
- Experience: Internships, co-op programs, or entry-level roles in civil or transportation engineering provide valuable hands-on experience.
Software Proficiency
- You will be able to use the relevant design software such as Civil 3D, Open Roads, MX, PDS/Key Line and Sign, AutoCAD, and ProjectWise
- Civil 3D, MicroStation V8i/ InRoads / Open Roads.
- Proficiency in Microsoft Excel and MS Office Suite,
- Knowledge of 12D and/or Site3D is a plus.
Career Path
A career in highway engineering involves planning highway construction and improvement projects. Before a road structure can be designed, the engineer must determine the exact route the road will take, how many paths are needed, how this road interfaces with other avenues, and how traffic flow will be carried.
Roadway design requires many considerations, including safety, convenience for bicyclists and pedestrians, parking facilities, calming traffic measures, pedestrian pathways, and drainage control on both paved and unpaved surfaces. Highway signs, guide rails before anything.
Typical Career Path
- Entry-Level/Graduate Engineer
Start by assisting senior engineers on tasks like drafting proposals, doing preliminary design work, and learning key software tools. - Mid-Level Highway Engineer
Manage smaller projects, supervise CAD teams, and communicate directly with clients and stakeholders. - Senior Highway Engineer/Project Manager
Oversee entire projects, manage budgets, mentor junior staff, and guide strategic decision-making. - Specialist/Consultant
Develop expertise in areas like ITS, pavement design, or sustainable engineering, offering specialized consulting services.
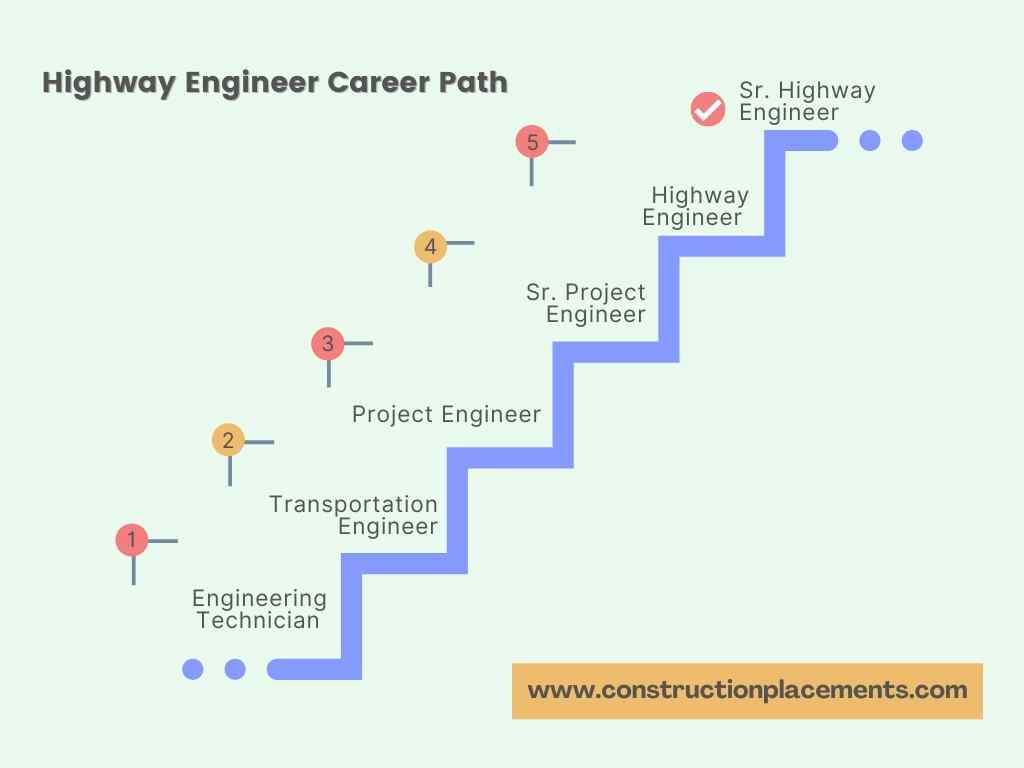
The above fig. shows the possible career path to become a highway engineer in a road construction company. A highway engineer has many enriching responsibilities, including one favorable aspect, which is to see the development you have worked on being built and operating successfully for years to come.
You will be involved in many projects, from minor proposals to complex projects of national importance, constructing new roads or upgrading existing highways.
You will work with different clients, including professional developers and public members. You will need to work with architectural consultants, planners, air quality and noise consultants, structural engineers, and quantity surveyors.
You’ll also need to meet with Local Planning and Highway Authorities and third parties like elected officials and residents during the planning process.
Suppose you have experience as a highways maintenance technician or highways maintenance operative. In that case, you could apply directly to a specialist civil engineering company to gain onsite experience as a trainee highways engineer.
You might start as an assistant to a more experienced highways engineer and progress as your abilities improve.
Essential Skills for Highway Engineers
Success in highway engineering requires both technical and soft skills:
Technical Proficiency
-
- Mastery of road design software: Civil 3D, AutoCAD, MicroStation, InRoads, OpenRoads
- In-depth understanding of highway design principles, traffic engineering, and drainage solutions
- Familiarity with construction standards, codes, and regulations
Analytical & Problem-Solving Abilities
-
- Ability to interpret traffic data and conduct feasibility studies
- Adapt designs to meet constraints related to geography, budget, and environmental standards
Project Management & Leadership
-
- Strong organizational skills to handle scheduling, delegating tasks, and reporting progress
- Experience with risk assessments, stakeholder negotiations, and resource planning
Communication & Collaboration
-
- Excellent verbal and written skills for reporting findings and discussing design modifications with multiple stakeholders
- Ability to work in interdisciplinary teams (planners, architects, environmental consultants)
Emerging Trends in Highway Engineering (2025 and Beyond)
- Smart Roads and Infrastructure: Intelligent highways equipped with real-time sensors to adjust traffic signals, monitor vehicle flow, and communicate with self-driving cars.
- Green & Sustainable Solutions: Increased focus on eco-friendly materials, low-carbon concrete, and green corridors to reduce carbon footprints.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPP): Collaboration between government agencies and private firms to fund large-scale infrastructural projects.
- Modular & Prefabricated Construction: Faster project completion through pre-built road sections and bridges that reduce on-site labor and environmental disruption.
- Advanced Data Analytics: Use of GIS, big data, and AI-driven models to accurately predict future traffic demands and optimize road networks.
Highway Engineer Salary and Compensation
- In India: The average salary for a Highway Engineer is around ₹385,664 per year (payscale.com). With experience, this can significantly increase, especially for those specializing in cutting-edge technologies or project management.
- In the United States: The average salary for a Highway Engineer is approximately $77,585 per year (payscale.com). Senior or specialized engineers can command six-figure salaries, depending on the region and complexity of the projects.
Factors Affecting Salary
- Location: Urban centers with high infrastructure demands typically offer higher pay.
- Experience & Specialization: Those with expertise in Intelligent Transportation Systems or sustainable designs are in high demand.
- Professional Licensure: A PE license often leads to higher-paying roles and leadership positions.
Companies Hiring Highway Engineers
- AECOM
- WSP
- Stantec, etc.
- Jacobs
- Arcadis
- Major Road and Highway Construction Firms (e.g., L&T, Gammon, NCC in India; Kiewit, Bechtel, Fluor in the US)
And all the major road and highway construction companies. Kindly check this list of the Best Road Construction Companies In India.
Working Locations for Highway Engineers
Highway engineers may work:
On-Site (Field Work)
-
- Directly supervising construction teams and inspecting ongoing projects.
- Facing varying weather conditions, ensuring compliance with design and safety standards.
In Office (Design & Planning)
-
- Using computer software for design, data analysis, budgeting, and stakeholder collaboration.
- Preparing proposals, reports, and official documentation.
Projects often dictate a mix of office and fieldwork, requiring flexibility and adaptability.
Soft Skills & Additional Competencies
- Time Management: Meeting strict deadlines requires excellent time management, especially on government-funded projects.
- Stakeholder Management: Negotiating with public officials, community leaders, and private developers.
- Team Collaboration: Coordinating with architects, planners, and environmental specialists.
- Continuous Learning: Staying updated with the latest design software, regulations, and sustainable building practices.
Challenges in Highway Engineering
- Budget Constraints
Balancing cost-effective solutions with high-quality designs. - Environmental Considerations
Mitigating pollution, preserving ecosystems, and handling climate change impacts. - Rapid Technological Changes
Keeping up with new software, construction methods, and best practices. - Public Scrutiny
Addressing community concerns over new highways or expansions that might affect local neighborhoods.
Required Skills
Extra skills which may benefit anyone considering a job as a highways engineer include:
- Ability to understand project requirements. Ability to take directions from senior engineers and execute them efficiently,
- Technical knowledge in all relevant areas of highway design,
- Effective communicator with excellent organization skills and the ability to work under tight schedules,
- Understanding of engineering science, maths, and technology
- Familiarity with building and construction
- Design skills
- Excellent verbal communication skills
- Analytical thinking skills.
Industry Outlook for 2025 and Beyond
The outlook for highway engineers remains strong thanks to global infrastructure initiatives and a focus on sustainable development. Notable factors shaping demand:
- Infrastructure Investment: Governments worldwide prioritize expanding and modernizing road networks to stimulate economic growth.
- Climate Resilience: Climate change drives the need for more robust, durable roads designed to withstand extreme weather events.
- Emerging Technologies: Self-driving cars and connected vehicles will require specialized infrastructure, opening fresh opportunities for innovation.
Highway engineering continues to be a forward-looking career with ample room for professional development, innovation, and the chance to make a lasting impact on communities.
Conclusion
A career in highway engineering offers a rewarding opportunity to shape the future of transportation networks. From the earliest planning stages to the final inspection of a roadway, highway engineers play a pivotal role in improving traffic flow, ensuring safety, and supporting economic development. As infrastructure evolves toward smart systems and eco-friendly designs, the demand for skilled highway engineers will only grow.
Whether you aspire to design safer roads, implement cutting-edge intelligent transport solutions, or lead massive construction projects, highway engineering provides a stable and fulfilling career path. By embracing lifelong learning, cultivating essential technical and soft skills, and staying updated with emerging trends, you can thrive as a highway engineer well into 2025 and beyond.
Related Posts:
- Best Civil Engineering Software Updated
- Best Road Construction Companies In India [Updated List 2025]
- Smart Road Technology: What it is, How it Works, and Where You Can See it Today?
- Contracts Engineer Job Description and Salary Details


