Last Updated on July 18, 2022 by Admin
Roads made entirely from plastic or plastic composites, and other elements are called plastic roads. Plastic roads differ from conventional roads in that conventional roads are formed of asphalt concrete, composed of asphalt and mineral aggregates. There are currently no known examples of conventional highways made entirely of plastic. However, plastic composite roads do exist and exhibit qualities above those of typical asphalt concrete roads, particularly better wear resistance. Using plastic on roads creates a new opportunity for post-consumer plastic recycling.
Since plastic roads are a relatively new concept, many building methods might be used. In Jamshedpur, India, bitumen, and plastic are combined to make the city’s roads. Collecting and managing the recycled plastic needed for these roadways is the first step in their construction. Most plastic used to construct these roadways is regular post-consumer waste, such as product packaging.
Plastic composites with other materials are used to construct plastic highways. Plastic roads differ from conventional roads in that conventional roads are formed of asphalt concrete, composed of asphalt and mineral aggregates. The introduction of plastic inroads also creates a new opportunity for post-consumer plastic recycling.
Professor Rajagopalan Vasudevan is an Indian plastic surgeon. His creative ideas include trying to use less plastic and recycle it, both of which are very beneficial to the environment. Chemistry professor Rajagopalan Vasudevan teaches at Madurai’s Thiagarajar College of Engineering.
This man uses leftover plastic to build a road. The plastic road is the name of this route. Plastic carry bags, mugs, and packaging for chips, cookies, and chocolates are just a few examples of plastic debris that can be utilized for road building.
Table of Contents
What is Plastic Road in construction?
Research has been done recently to help decrease the amount of waste plastic on the planet and promote its use in paving improvements. According to related experimentation, when waste plastic is introduced to heated aggregate, it coats the aggregate with a thin layer of plastic. When this mix is formed with the binder, it is discovered to have more muscular strength, higher water resistance, and better performance over time.
Therefore, it makes sense to use waste plastic for building roadways. The use of plastic lengthens the bitumen’s melting point and helps the road maintain its flexibility over the winter. Waste plastic that has been shredded into little pieces works well as a binder for bitumen aggregates. The CSIR-Central Road Research Institute has advocated using plastic waste in asphalt road construction.
Plastic carry bags, throwaway cups, and bottles salvaged from landfills are mainly used as a component of the construction material for plastic highways. Plastics melt when combined with hot bitumen to form an oily coating over the aggregate, then placed on the road surface like a typical bitumen road.
Polyethylene terephthalate, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polypropylene (PP), and high- and low-density polyethylene are some of the plastics that are most frequently used in packaging (HDPE and LDPE). To begin with, these elements are separated from plastic garbage. The material is cleaned, dried, and shredded after sorting. At about 170°C, the plastic is combined and melted. The melted plastic is then combined with hot bitumen. After mixing, the mixture is laid as one would with conventional asphalt concrete.
There are currently no known examples of conventional highways made entirely of plastic. However, plastic composite roads do exist and exhibit qualities above those of typical asphalt concrete roads, particularly better wear resistance.
How to construct the Plastic Road?
The following list of the numerous steps in building a plastic road.
- Gathering waste plastics, such as laminated plastics, carry bags, mugs, and soft and hard foams.
- Washing it to clean it.
- Slicing it into uniform-sized pieces.
- Melting the waste plastics at 165°C, mixing them with bitumen and heated aggregates, and laying the road with the resulting mixture.
The whole procedure is really easy. The waste plastic is first to cut into small pieces using a shredding machine. After that, the bitumen is heated to 160°c to achieve a strong bond, and the heated aggregate mix is passed to the mixing chamber. Keeping an eye on the temperature while heating is crucial.
The aggregate is then supplemented with scrap plastic. It evenly coats the aggregate within 30 to 60 seconds, giving it an oily appearance. The gravel coated with plastic trash is combined with hot bitumen, and the resulting mixture is utilized to build roads. The temperature for laying roads ranges from 110°C to 120°C. The roller in use can support 8 tonnes.
Process of Waste plastic road constructions
The reasons why plastic garbage must be used in road construction are explained in the paragraphs below.
- Hot Aggregate—The material was heated to about 1700°C.
- Plastic-coated aggregate (hot aggregate plus shredded waste plastic). Shredded plastic garbage has a size range of 2.36 mm to 4.75 mm.
- Plastic Coated Aggregate Bitumen Mixture (Plastic Coated Aggregate + Hot Bitumen 160 0C) – To ensure a consistent distribution, the shredded plastic waste was placed over hot aggregate while constantly mixed. After becoming softer, the plastic was coated over the aggregate.
- Ready supplies Laying at 120 0C: Hot aggregate coated with plastic trash was combined with hot bitumen of grades 60/70 or 80/100.
- Central mixing plant: This aids in improved temperature control and material mixing to provide a uniform coating before heated bitumen is sprayed on the road.
The two primary processes are the dry process and the wet procedure.
Dry Process: Instead of burning the plastic, the dry process softens it before using it as a coating material. Hot bitumen (160°C) and heated stone aggregate are combined to create a flexible pavement, and the resulting mixture is utilized to lay roads. The performance of the pavement is improved when the aggregate is coated with polymers because it improves the aggregate’s quality in terms of voids, soundness, and moisture absorption and reduces porosity.
Wet Process: Plastic garbage is powdered after being pulverized. At 160°C, waste plastic is added to the bitumen in powder form. A high-shear blender is necessary to prepare plastic-modified bitumen, and a particular chemical treatment would be needed to prevent phase separation. Wet processing was not used since the procedure does not produce a homogeneous mix with distinct separated solid deposits.
The dry process is the most common waste plastic technique in road construction.
Properties of Plastic Road
They are more realistic because of the following qualities of plastic roads:
- Plastic roadways might include heating and power generation. Heating can assist drain water from the surface and stop
- roadways from freezing.
- Since plastics have a variety of chemical and physical characteristics, roadways can be designed to fit particular specifications (e.g., weather and wear resistance)
- The problem of plastic trash in landfills and oceans around the world may be resolved by mixing plastic garbage in asphalt at a ratio of 8%, which will soon increase in value as a commodity in underdeveloped nations.
- Interlocking plastic road parts that can be rapidly put together or taken down can be created. The on-site building is now considerably more streamlined and practical. Lower costs are also related to the simplicity and speed of road construction.
- Most waste plastic is often disposed of in landfills, burned, or polluted into the environment, which can be used to construct plastic roadways. Plastic waste management techniques that involve either landfilling or incineration present challenges. Plastics can release contaminants into the soil around landfills, and burning plastic releases gaseous pollutants like carbon dioxide.
- Why Plastic may be reused more often on roads made of plastic-bitumen composites since there is no need to be particularly picky about the plastics used. Most plastic garbage is not recycled because it is frequently combined with other plastic and non-plastic debris, and there is currently no simple way to separate the waste without a lot of labor.
- Less asphalt use conserves resources. Asphalt concrete needs petroleum, which is getting harder to come by.
- Less asphalt is utilized when building roads because of the usage of plastic. Since 2% of the world’s carbon emissions come from asphalt, this is good for the environment.
- Asphalt is significantly more difficult to work with than modular plastic components.
- Plastic can be used to make asphalt, making the mixture less viscous. As a result, operating temperatures can be lowered, reducing VOC and CO emissions.
- Roads made of plastic and bitumen offer more wear resistance than conventional asphalt concrete roads. They are less prone to rutting and require less maintenance because they do not absorb water and are more flexible. Road surfaces retain their smoothness, require less upkeep, and are better at absorbing sound.
- Economical: Post-consumer recycled plastics are more affordable than asphalt.
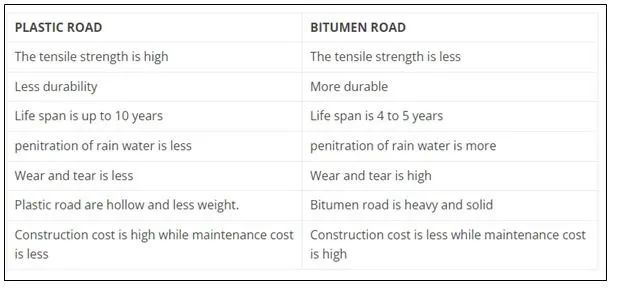
Difference between Plastic roads and Bitumen roads
One of the better alternatives to traditional roadways is plastic pavement. Regarding durability, strength, and other factors, they differ significantly.
Compared to roads made of asphalt made from a regular mix, the durability of roads made of shredded plastic waste is significantly higher. It has been discovered that plastic waste-mixed roads perform better than traditional ones. In addition to adding strength to support heavier loads, plastic’s binding ability prolongs the road’s lifespan. It is stated that plastic-bitumen roads can endure up to 10 years, whereas a typical “highway quality” road lasts four to five years.
Rainwater won’t permeate the tar due to the plastic in it. This technique will thereby reduce the need for road repairs. Additionally, employing plastic will help minimize non-biodegradable trash because each km of road with an average width takes over two tonnes of polyblend. Construction of roads with plastic can cost a little more than traditional methods. Adopting the technology shouldn’t be discouraged, as the advantages outweigh the drawbacks.
..
Advantages of Plastic Road
Roadside plastic trash Construction aids the nation’s economic prosperity in addition to advancing technology:
- A compact prefabricated building
- Quicker construction and shorter maintenance periods
- Better performance and a longer lifespan
- Requires little to no upkeep. The substance is essentially resistant to environmental factors like weather and weeds.
- The innovation is much more environmentally friendly.
- The Plastic Road will be made entirely of recycled plastic and completely reusable. It fully complies with the circular economy’s guiding principles and the Cradle-to-Cradle philosophy.
- Making use of two spaces. The design’s hollow chamber can be used to house cables and pipes or to store water.
- The potential for ongoing security and water drainage
- The entire area near the road may be prefabricated.
- The idea presents possibilities for additional innovation. Examples include light poles, traffic loop sensors, and solar-heated highways.
- Contribution to the issue of plastic waste in society
Downloads:
- Civil Engineering Interview Questions and Answers PDF eBOOK
- Mostly Asked Mechanical Engineering Interview Questions and Answers
- How To Face A Technical Interview
- Effective Job Search Strategies for Engineers
- Top 50 HR Interview Questions and Answers for Engineers
- Civil Engineering Careers Blueprint eBook: The Great Construction Career
Disadvantages of Plastic Road
Currently, burning most of the plastic trash results in the emission of poisonous fumes into the atmosphere, making the process of treating plastic waste hazardous to the environment. Here are a few drawbacks of plastic roads:
- The toxic substances mixed with the plastic debris would begin to leach.
- But HCL gas will undoubtedly be released if chlorine is present.
- One of the main drawbacks of plastic is the cleaning process. Because it includes poisonous materials.
- When the plastic melts, structural weaknesses could develop, leading to premature failure.
- Chlorine will cause the laying process to create a fatal gas.
- The price of the building is high.
- Because there is limited water penetration, the groundwater table is impacted.
Future trends for Plastic Roads
The municipal department gathers the plastic garbage from all types of locations, including residential, commercial, industrial, institutional, etc., and transports it to dump yards, a landfill, or an incinerator. All of them have adverse environmental effects. High pollution levels from incinerating waste led to a wide range of illnesses in humans and animals. Landfilling plastic trash reduces the soil’s natural qualities, and dump yards take up a lot of space, preventing a specific location from being developed in the future.
Plastic is the primary cause of all the aforementioned issues. Hence it must be recycled or utilized again. In conclusion, all the plastic garbage can be preserved separately and then sent for reuse in road construction. If all these procedures are followed, road building will be economical and practical, and there will be less plastic, a better environment, and better roads.
Conclusion
Waste plastics are being produced at an ever-increasing rate. The three main polymers—polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene—show adhesion properties in their molten state. Plastics will raise the bitumen’s melting point. Therefore, one of the most significant ways to quickly dispose of waste plastics is to utilize them for pavement.
Utilizing cutting-edge technologies improved road construction while also lengthening its lifespan and providing a revenue stream. Plastic roads would be a godsend for India’s hot and oppressively humid climate, where temperatures regularly exceed 50°C and torrential rains cause havoc and leave most of the roads with large potholes.
With the usage of waste plastic in roadways, it is anticipated that India will soon have robust, long-lasting, and environmentally friendly roads that would free the nation of all types of plastic trash. The government urgently needs sound planning and a waste management system to make widespread and successful use of this technology.


