Last Updated on June 12, 2024 by Admin
Have you ever wondered how products seamlessly arrive at your doorstep just days after placing an order? This remarkable efficiency is largely thanks to logistics analysts, the unsung heroes of supply chains. Becoming a logistics analyst might be your perfect fit if you’re interested in a career that combines data analysis with real-world impact. This guide will explore what logistics analysts do, the skills and education needed, career growth opportunities, and salary insights.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Role of a Logistics Analyst

Job Description
A logistics analyst analyzes and optimizes an organization’s supply chain operations. They ensure that products are delivered on time and most cost-effectively. This involves evaluating data to identify inefficiencies, developing strategies to improve processes, and collaborating with various departments to implement these strategies. Logistics analysts work in multiple industries, including manufacturing, retail, and transportation.
Key Responsibilities
The responsibilities of a logistics analyst can vary depending on the industry and specific role. However, some common duties include:
- Data Analysis: Collecting and analyzing data related to supply chain processes, including inventory levels, transportation costs, and delivery times.
- Process Improvement: Identifying areas for improvement within the supply chain and developing strategies to enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
- Reporting: Creating detailed reports and presentations to communicate findings and recommendations to management.
- Collaboration: Working closely with other departments, such as procurement, production, and sales, to ensure that supply chain processes align with overall business goals.
- Technology Implementation: Utilizing software and technology to streamline logistics operations and improve data accuracy.
- Compliance: Ensuring that supply chain operations comply with relevant laws and regulations.
Growth Opportunities in Logistics
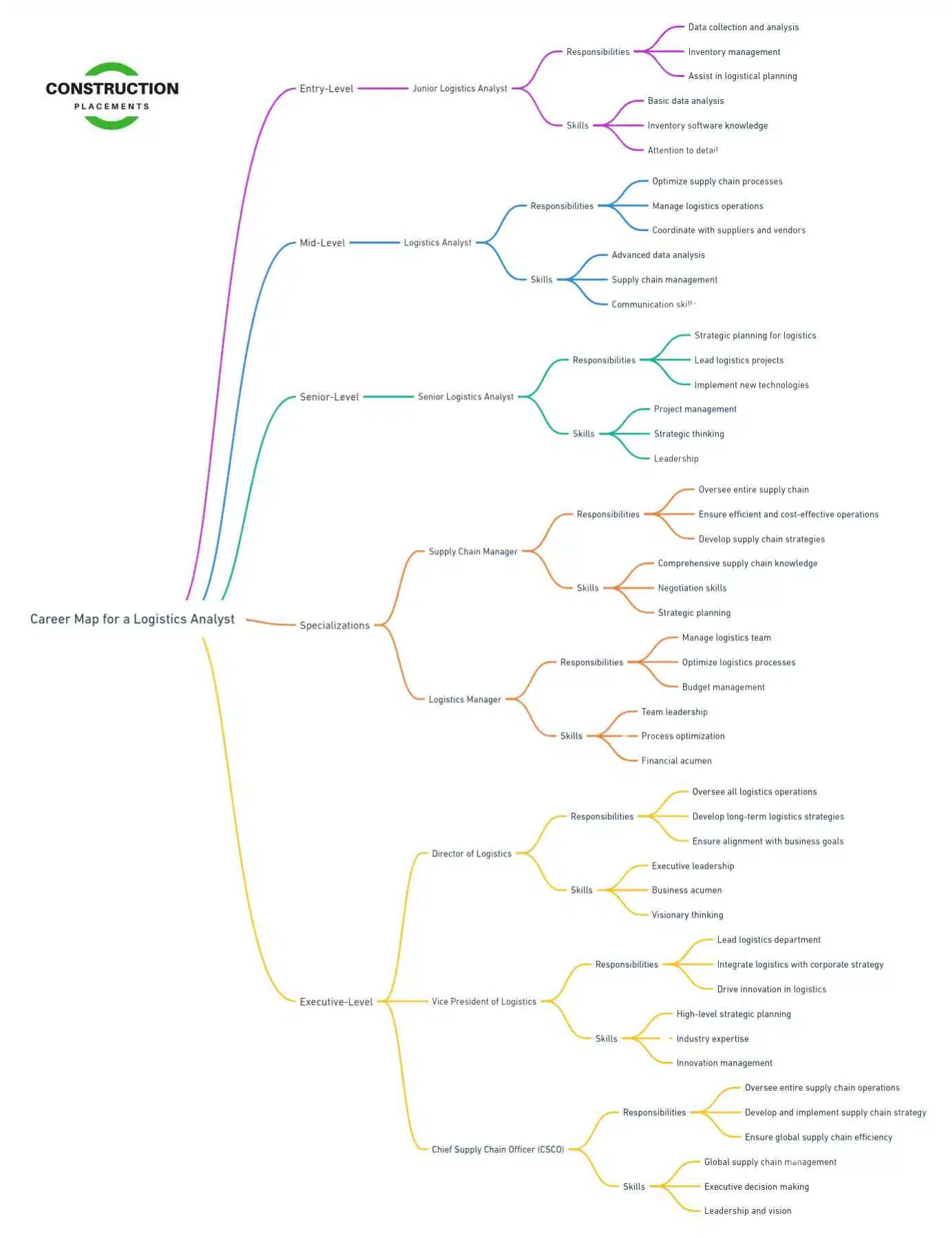
Career Pathways
A career as a logistics analyst can lead to various advanced roles within the supply chain and logistics field. Some potential career pathways include:
- Senior Logistics Analyst: With experience, you can advance to a senior logistics analyst position, where you’ll take on more complex projects and have greater responsibility.
- Logistics Manager: In this role, you’ll oversee the entire logistics operation, managing a team of analysts and other logistics professionals.
- Supply Chain Manager: This position involves overseeing the entire supply chain, from procurement to delivery, ensuring that all processes run smoothly.
- Operations Manager: As an operations manager, you’ll be responsible for the overall efficiency of the organization’s operations, including logistics, production, and quality control.
- Consultant: Experienced logistics analysts can also work as consultants, providing expert advice to organizations looking to improve their supply chain operations.
Industry Demand
The demand for logistics analysts is expected to grow as companies seek ways to optimize their supply chains and improve efficiency. The rise of e-commerce, globalization, and technological advancements contribute to this increased demand. As companies strive to remain competitive in the global market, the need for skilled logistics professionals will continue to rise.
Related Courses:
- Introduction to Portfolio Construction and Analysis with Python
- Future Development in Supply Chain Finance and Blockchain Technology
- Technology Entrepreneurship
- The Construction Industry: The Way Forward
Essential Skills for Logistics Analysts
Technical Skills
- Data Analysis: Proficiency in analyzing large datasets to identify trends and make data-driven decisions is crucial. This includes using software tools such as Excel, SQL, and specialized logistics software.
- Supply Chain Management: A deep understanding of supply chain principles, including procurement, inventory management, transportation, and distribution.
- Project Management: The ability to manage projects from inception to completion, including planning, execution, and monitoring.
- Information Technology: Familiarity with IT systems and software used in logistics, such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems, TMS (Transportation Management Systems), and WMS (Warehouse Management Systems).
Soft Skills
- Problem-Solving: The ability to identify issues within the supply chain and develop effective solutions.
- Communication: Strong verbal and written communication skills are essential for collaborating with team members and presenting findings to management.
- Attention to Detail: A meticulous approach to analyzing data and implementing strategies to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
- Analytical Thinking: The capability to break down complex problems and analyze them systematically.
- Adaptability: The ability to adapt to changing circumstances and handle unexpected challenges in a dynamic environment.
Educational Requirements
Degree Programs
To become a logistics analyst, a bachelor’s degree in a relevant field is typically required. Some of the most common degree programs for aspiring logistics analysts include:
- Logistics and Supply Chain Management: This program provides a comprehensive understanding of logistics principles, supply chain management, and related technologies.
- Business Administration: A degree in business administration with a focus on operations or supply chain management can also be beneficial.
- Industrial Engineering: This program focuses on optimizing complex processes and systems, making it highly relevant for logistics analysts.
- Operations Management: This degree program covers various aspects of managing and improving business operations, including logistics and supply chain management.
Certifications
In addition to a degree, obtaining professional certifications can enhance your credentials and improve your job prospects. Some of the most recognized certifications in the logistics field include:
- Certified Supply Chain Professional (CSCP): Offered by APICS, this certification covers the entire supply chain process, from planning to execution.
- Certified Logistics Professional (CLP): This certification, offered by the International Society of Logistics, focuses on logistics and transportation management.
- Six Sigma Certification: Six Sigma methodologies are widely used in logistics to improve processes and reduce defects. Obtaining a Six Sigma certification can be highly beneficial.
- Project Management Professional (PMP): Project management skills are essential for logistics analysts, and this certification demonstrates your ability to manage projects effectively.
Here is the online video lecture series on learning Logistics Analytics for FREE.
Continuing Education
The logistics field constantly evolves, and staying updated with the latest trends and technologies is crucial. Continuing education through workshops, seminars, and online courses can help you stay current and advance your career. Some reputable sources for continuing education include:
- APICS: Offers a variety of courses and certifications related to supply chain and logistics management.
- Council of Supply Chain Management Professionals (CSCMP): Provides educational resources, conferences, and certifications for logistics professionals.
- Institute of Supply Management (ISM): Offers courses and certifications focused on supply chain management and procurement.
Job Outlook for Logistics Analysts

Employment Projections
The job outlook for logistics analysts is positive, with steady growth expected in the coming years. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), employment of logisticians, which includes logistics analysts, is projected to grow 4 percent from 2022 to 2032, about as fast as the average for all occupations. This growth is driven by the increasing complexity of supply chains and the need for companies to optimize their operations.
Industry Trends
Several trends are shaping the future of the logistics industry and influencing the demand for logistics analysts:
- E-commerce Growth: The rapid expansion of e-commerce has significantly increased the need for efficient logistics and supply chain management. Companies must ensure timely product delivery to meet customer expectations, driving demand for skilled logistics analysts.
- Technological Advancements: Adopting advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain is transforming the logistics industry. Logistics analysts with expertise in these technologies will be in high demand.
- Sustainability: There is a growing focus on sustainability in supply chain operations. Companies seek ways to reduce their environmental impact, and logistics analysts play a crucial role in developing and implementing sustainable practices.
- Globalization: As companies expand their operations globally, managing complex international supply chains becomes essential. Logistics analysts are needed to navigate the challenges of global logistics and ensure smooth operations.
Salary Insights
Average Salary
The salary of a logistics analyst can vary based on factors such as experience, education, location, and industry. According to the BLS, the median annual wage for logisticians, including logistics analysts, was $79,400 in May 2023. The lowest 10 percent earned less than $47,990, while the highest 10 percent earned more than $128,550.
Factors Influencing Salary
Several factors can influence the salary of a logistics analyst:
- Experience: As with most professions, experience plays a significant role in determining salary. Entry-level logistics analysts can expect to earn less than their more experienced counterparts. With experience, professionals can move into higher-paying positions and take on more responsibilities.
- Education: Higher levels of education, such as a master’s degree or relevant certifications, can lead to higher salaries. Employers often value advanced education and specialized knowledge.
- Industry: The industry in which a logistics analyst works can also impact salary. For example, logistics analysts in the manufacturing and technology sectors may earn higher salaries compared to those in retail or transportation.
- Location: Geographic location can significantly affect salary levels. Logistics analysts working in metropolitan areas or regions with a high cost of living tend to earn higher salaries than those in rural areas.
Salary by Industry
The salary of logistics analysts can vary across different industries. Here are some examples of median annual wages for logisticians in various sectors, according to the BLS:
- Federal Government: $86,540
- Manufacturing: $77,980
- Professional, Scientific, and Technical Services: $75,950
- Wholesale Trade: $73,280
- Transportation and Warehousing: $70,180
Steps to Becoming a Logistics Analyst

1. Obtain a Relevant Degree
The first step in becoming a logistics analyst is to obtain a bachelor’s degree in a relevant field such as logistics and supply chain management, business administration, industrial engineering, or operations management. These programs provide a strong foundation in logistics principles, data analysis, and supply chain management.
2. Gain Practical Experience
While pursuing your degree, gaining practical experience through internships or part-time jobs in logistics or supply chain management can be highly beneficial. Practical experience allows you to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios and develop essential skills.
3. Develop Technical Skills
Proficiency in data analysis, supply chain management software, and project management tools is crucial for logistics analysts. Take advantage of courses and workshops to develop these technical skills and stay updated with the latest technologies.
4. Obtain Certifications
Earning professional certifications such as CSCP, CLP, Six Sigma, or PMP can enhance your credentials and improve your job prospects. These certifications demonstrate your expertise and commitment to the field.
5. Build a Professional Network
Networking is essential for career growth in any field. Join industry associations, attend conferences, and participate in online forums to connect with other professionals and stay informed about industry trends and opportunities.
6. Apply for Entry-Level Positions
Once you have obtained your degree and gained some practical experience, start applying for entry-level logistics analyst positions. Tailor your resume to highlight your relevant skills, education, and experience.
7. Continue Learning and Advancing
The logistics field is constantly evolving, and continuous learning is essential for career advancement. Stay updated with the latest trends, technologies, and best practices through continuing education and professional development opportunities.
Conclusion
Becoming a logistics analyst offers a rewarding career path with numerous opportunities for growth and advancement. By understanding the job description, responsibilities, required skills, educational requirements, job outlook, and salary insights, you can make informed decisions and take the necessary steps to succeed in this dynamic field. With the right education, experience, and dedication, you can embark on a fulfilling career as a logistics analyst, contributing to the efficiency and success of supply chains across various industries.
Related Posts:
- Supply Chain Analyst Job Description & Career Guide
- Supply Chain Management and Logistics: The Ultimate Career Guide
- How to Become a Business Analyst in 2024?
- Why a Career as a Sustainability Analyst is the Future of Green Jobs
- Become a Data Analyst: A Future Proof Career Option [2024 Career Guide]


