Last Updated on September 9, 2025 by Admin
India’s construction sector stands at the threshold of unprecedented growth, with industry projections indicating the creation of up to 30 million new jobs by 2030. This massive expansion will bring total construction employment to approximately 100 million workers, making construction one of India’s largest employment generators after agriculture.
ConstructionCareerHub App is LIVE — built ONLY for construction careers. Don’t apply with a weak resume.
Get ATS-ready Resume Lab + Interview Copilot + Campus Placement Prep (resume screening, skill gaps, interview readiness) — in minutes & Other advanced features.
Explore Smarter Construction Career Tools →Quick check. Big impact. Start now.
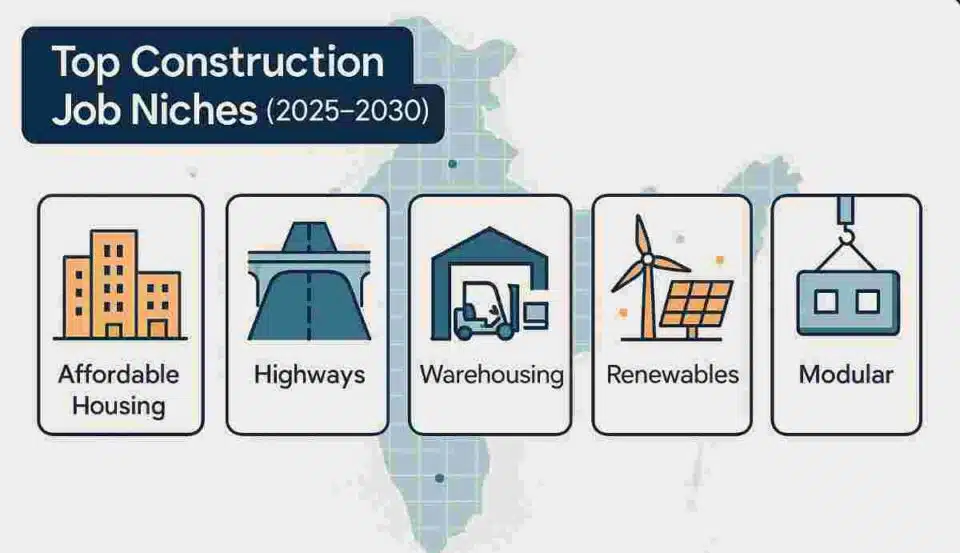
For construction professionals, job seekers, and industry stakeholders, understanding which niches will drive this growth is crucial for career planning and business strategy. This comprehensive analysis examines the five key construction segments that will generate the majority of new opportunities: affordable urban housing, transport infrastructure, logistics and warehousing, renewable energy projects, and modular construction.
Table of Contents
Construction Job Market Overview: The Numbers That Matter
The construction industry’s job creation potential is staggering. According to Knight Frank’s comprehensive market analysis, India’s real estate and construction sector alone will employ approximately 100 million people by 2030, representing a 30 million increase from current levels.
This growth spans all skill categories:
- Unskilled laborers: Site preparation, material handling, basic construction tasks
- Semi-skilled tradespeople: Masons, carpenters, electricians, machine operators
- Skilled professionals: Engineers, surveyors, quality inspectors, project managers
- Specialized experts: BIM coordinators, renewable energy technicians, automation specialists
The National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP) envisions investing ₹111 lakh crore in infrastructure projects by 2025, with roads commanding approximately 18% of this massive allocation.
1. Affordable Urban Housing: The Employment Powerhouse
PMAY-U: Transforming Urban India Through Job Creation
The Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana–Urban (PMAY-U) represents India’s most ambitious housing initiative, targeting 20 million urban homes by 2026. With 1.18 crore houses already sanctioned and over 89 lakh completed, this program exemplifies large-scale job creation in action.
The introduction of PMAY-U 2.0 in September 2024 adds another 10 million affordable homes to the pipeline, ensuring sustained employment demand through the decade. Each housing project creates a multiplier effect: every 100-unit development employs dozens of skilled tradespeople alongside engineering and management professionals.
Job Opportunities Across Skill Levels
Semi-Skilled Trades (High Demand)
- Civil masons and bricklayers for structural work
- Carpenters for formwork and finishing
- Electricians for wiring and electrical installations
- Plumbers for water supply and sanitation systems
- Steel fixers for reinforcement work
Each housing unit represents 2-3 direct construction jobs during its build cycle, translating the 20 million homes target into tens of millions of person-jobs for skilled and semi-skilled workers.
Skilled Engineering Roles
- Site engineers for construction supervision
- Surveyors for layout and measurement
- Quality inspectors ensure compliance with building codes
- Town planners for project design and approvals
- Architects specializing in affordable housing design
Professional Management Positions
- Project managers overseeing multiple housing developments
- Procurement officers managing material supply chains
- Compliance officers ensure adherence to PMAY-U guidelines
- Finance managers handling public-private partnerships
- Community engagement specialists
The social impact extends beyond job numbers. PMAY-U projects prioritize local labor engagement, creating livelihood opportunities in urban and peri-urban areas while contributing to skill development in local communities.
2. Roads, Highways & Expressways: Infrastructure’s Employment Engine
Mega Infrastructure Investment Driving Job Growth
India’s transport infrastructure sector is experiencing unprecedented investment levels. The National Infrastructure Pipeline allocates roughly ₹20 lakh crore to road development, representing the single largest component of infrastructure spending alongside energy.
The Bharatmala Pariyojana Phase-I alone covers 34,800 km of national highways with an investment of ₹5.35 lakh crore. Government estimates indicate this program will generate approximately 14.2 crore man-days of employment during implementation—equivalent to over 50,000 full-year jobs annually.
Diverse Employment Opportunities in Highway Construction
Engineering and Technical Staff (200,000+ positions needed)
- Civil engineers for project design and supervision
- Highway designers using advanced CAD systems
- Survey engineers with GPS and LiDAR expertise
- Geotechnical experts for soil analysis and foundation design
- Material testing specialists for quality assurance
- CAD technicians for technical drawing and documentation
Highway construction demands sophisticated technical expertise, with site laboratories established on major projects requiring qualified technicians and engineers for continuous quality monitoring.
Machine Operators and Skilled Trades (1 million+ positions)
- Heavy equipment operators (excavators, bulldozers, graders)
- Asphalt paving machine operators
- Crane operators for bridge construction
- Plant mechanics for equipment maintenance
- Certified welders for structural steel work
- Blasters for rock cutting and excavation
The mechanized nature of modern road construction drives substantial demand for trained operators. Industry reports show construction equipment sales rising approximately 20% annually, indicating proportional growth in operator employment.
Manual Labor and Support Roles (5+ million positions)
- Site preparation and clearing crews
- Drainage system installation teams
- Material handling and transport workers
- Traffic management personnel
- General construction laborers
These positions provide crucial employment for rural workers and migrants, with major highway projects typically engaging 500-1000 laborers per 50-km stretch during peak construction phases.
The sector’s growth creates significant multiplier effects, with every direct highway construction job supporting approximately three additional positions in materials production, logistics, and related services.
3. Logistics & Warehousing: Building India’s Digital Economy Infrastructure
Modern Warehousing: Meeting E-commerce and Manufacturing Demands
India’s warehousing sector transformation from traditional godowns to sophisticated logistics facilities reflects the country’s economic evolution. Industry projections indicate steady expansion at approximately 4% CAGR, with potential demand reaching 159 million sq ft by 2047, up from current levels of 60-70 million sq ft.
The National Logistics Policy 2022 and Multi-Modal Logistics Parks (MMLP) development—with 15 projects currently in progress—further accelerate this growth trajectory.
Specialized Job Categories in Logistics and Construction
Warehouse Construction Teams
- Steel erectors for pre-engineered building assembly
- Racking system installers for storage solutions
- Docking bay construction specialists
- Fire safety system installers
- HVAC technicians for climate control
- Electrical specialists for warehouse lighting and power
Modern warehouse construction (often exceeding 1 lakh sq ft) requires specialized crews capable of rapid deployment. A single large fulfillment center typically employs 300-500 construction workers at peak activity.
Cold-Chain and Automation Specialists
- Insulated panel installers for refrigerated facilities
- Ammonia refrigeration system technicians
- Automation integration engineers for sortation systems
- Material handling equipment installers
- Industrial IT systems specialists
- Robotics commissioning technicians
The rise of automated distribution centers and cold storage facilities creates demand for cross-disciplinary skills combining construction expertise with mechatronics and industrial engineering knowledge.
Logistics Development Professionals
- Logistics park project managers
- Industrial architecture specialists
- Supply chain network analysts
- GIS planners for optimal site selection
- Environmental compliance specialists
The sector’s PE investment of approximately $1.5 billion in 2022 demonstrates strong confidence and ensures continued project pipeline development.
4. Renewable Energy Infrastructure: Engineering the Green Transition
Massive Scale Renewable Energy Deployment
India’s renewable energy targets represent one of the world’s most ambitious green transitions. The goal of 500 GW renewable capacity by 2030—accounting for over 40% of new electricity generation—creates unprecedented construction opportunities.
With renewable capacity already surpassing 209 GW by the end of 2024 (45% of total capacity), the momentum is evident. The International Labour Organization estimates that India’s green economy transition could add 3 million renewable energy jobs by 2030.
Green Jobs Across the Skills Spectrum
Solar Park Development
- Land preparation and grading crews
- Foundation and piling specialists for mounting structures
- Solar panel installation teams
- Cable trenching and electrical connection crews
- Inverter station construction workers
Utility-scale solar parks spanning thousands of acres employ thousands of workers during peak construction. Each 1 MW of solar capacity creates 3-5 construction and commissioning jobs, with India targeting approximately 280 GW of solar by 2030.
Wind Farm Construction
- Heavy civil construction crews for turbine foundations
- Steel fixing specialists for concrete pedestals
- Formwork carpenters for foundation construction
- Crane operators for turbine assembly
- Transmission line installation teams
Each large wind turbine foundation requires approximately 30 tons of steel and 240+ cubic meters of concrete, creating substantial labor-intensive work in often remote locations.
Professional and Technical Roles
- EPC project managers for renewable projects
- Electrical engineers specializing in grid integration
- Commissioning experts for complex renewable systems
- Operations and maintenance planners
- Energy storage system integrators
The renewable sector faces a significant talent shortage for specialized roles, creating excellent career opportunities for professionals willing to develop green energy expertise.
Long-term operations and maintenance requirements add another layer of stable employment, with approximately 7 O&M jobs sustained per MW of solar capacity over facility lifetimes.
5. Modular & Prefabricated Construction: The Future of Building
Technology-Driven Construction Innovation
Modular construction represents a fundamental shift in how India builds, addressing productivity challenges in traditional construction where only 19% of the 71 million construction workers are formally skilled. Market analysis projects approximately 7.4% CAGR growth for prefabricated construction through 2030, significantly outpacing traditional methods.
Leading companies like L&T and Tata Projects are establishing prefab manufacturing facilities, while government initiatives including Light House Projects under GHTC promote adoption of these advanced techniques.
New Job Categories in Modular Construction
Factory Production Roles
- Precast concrete component operators
- Steel modular structure fabricators
- Quality control inspectors for manufactured components
- Rebar bending machine operators
- 3D printing construction technicians
Factory-based construction work offers more controlled environments and consistent employment compared to traditional site-based roles, typically providing better training opportunities and working conditions.
Logistics and Assembly Specialists
- Just-In-Time delivery coordinators
- Heavy transport drivers for oversized modules
- Crane operators specializing in module installation
- Assembly crew supervisors
- Module alignment and connection specialists
Modular construction’s success depends heavily on precise logistics coordination and skilled assembly teams capable of rapid, accurate installation.
Digital Construction Professionals
- BIM coordinators for modular design integration
- Design for Manufacture and Assembly (DfMA) engineers
- Virtual construction simulation specialists
- Modular project managers
- Construction technology software specialists
The integration of digital design with manufacturing processes creates demand for professionals combining traditional construction knowledge with advanced software skills.
Case studies demonstrate modular construction’s impact: L&T’s precast implementation reduced on-site manpower by 30% while accelerating construction schedules. However, this reduction in site labor corresponds to increased factory employment, redistributing rather than eliminating jobs while improving productivity and working conditions.
Strategic Career Guidance for Construction Professionals
Positioning Yourself for Growth Markets
For Entry-Level Professionals:
- Consider specializing in renewable energy or modular construction for future-proof career paths
- Pursue technical certifications in emerging areas like BIM, green building, or automation systems
- Gain experience in affordable housing projects to develop mass construction expertise
For Mid-Career Professionals:
- Develop project management skills for large infrastructure projects
- Consider cross-training in logistics and warehousing construction
- Pursue advanced certifications in specialized areas like highway engineering or renewable energy
For Senior Professionals:
- Focus on developing expertise in emerging construction technologies
- Consider leadership roles in government flagship programs
- Develop capabilities in sustainable construction and green building practices
Skills Development Priorities
The construction industry’s evolution demands continuous learning. Priority areas include:
- Digital construction technologies (BIM, IoT, automation)
- Sustainable construction practices and green building
- Modular construction and prefabrication techniques
- Project management in complex infrastructure projects
- Quality assurance and regulatory compliance
Government initiatives like Skill India and the Skill Council for Green Jobs provide structured training pathways for these emerging competencies.
Industry Outlook: Challenges and Opportunities
Market Drivers Supporting Sustained Growth
Several factors ensure robust construction employment through 2030:
- Government Policy Support: Continued investment in housing and infrastructure
- Economic Growth: India’s path to a $5 trillion economy requires substantial infrastructure
- Urbanization: Rapid urban growth is driving housing and infrastructure demands
- Technology Adoption: Modernization is creating new specialized job categories
- Sustainability Focus: Green building and renewable energy mandates
Addressing Industry Challenges
The construction sector faces several challenges that present opportunities for prepared professionals:
- Skills Gap: Shortage of formally trained workers creates premium opportunities for skilled professionals
- Technology Integration: Need for workers comfortable with digital construction tools
- Safety Standards: Increasing focus on workplace safety requires specialized expertise
- Regulatory Compliance: Complex approval processes demand knowledgeable professionals
Recent industry forecasts show some moderation in growth projections. ICRA revised construction growth estimates to 6-8% from earlier 8-10% projections due to temporary delays in road project awards. However, the fundamental drivers remain strong, and this adjustment represents timing rather than fundamental demand changes.
Conclusion: Capitalizing on India’s Construction Boom
India’s construction industry from 2025 to 2030 presents extraordinary opportunities across all skill levels and specializations. The five key niches—affordable housing, transport infrastructure, logistics and warehousing, renewable energy, and modular construction—will collectively drive the creation of tens of millions of jobs while transforming India’s physical infrastructure.
For construction professionals and job seekers, this period offers:
- Diverse Career Paths: Opportunities spanning from traditional trades to cutting-edge technology roles
- Geographic Spread: Projects across urban, rural, and remote locations
- Skill Development: Access to training in emerging construction technologies
- Economic Stability: Long-term project pipelines providing sustained employment
- Social Impact: Participation in nation-building initiatives with measurable societal benefits
The construction sector’s evolution toward technology integration, sustainability focus, and modular approaches creates new professional pathways while maintaining demand for traditional skills. Success in this environment requires adaptability, continuous learning, and strategic career positioning in high-growth niches.
With proper preparation and skill development, construction professionals can leverage this unprecedented growth phase to build rewarding careers while contributing to India’s infrastructure transformation. The scale of opportunity—from government infrastructure projects creating 5 million jobs annually to the warehousing sector’s massive expansion—ensures that well-prepared professionals will find abundant opportunities in India’s construction boom.
The future belongs to construction professionals who can adapt to evolving technologies while maintaining expertise in fundamental building skills. By focusing on the five key growth niches identified in this analysis, industry professionals can position themselves at the forefront of India’s infrastructure revolution.
Related Posts:
- Unveiling Modular Construction Costs: A Comprehensive Guide to Modern Building Economics
- Highway Engineer Job Description and Salary Details
- The Ultimate Guide to Warehouse Inventory Systems
- What does automation for warehouse operations look like in 2025?