Last Updated on April 24, 2025 by Admin
Every year, thousands of civil engineering graduates in India don crisp caps and receive their degrees—ready to “build the nation.” Yet the moment they step onto a live construction site, theory meets hard reality: supervisors expect them to hit the ground running on tasks never covered in college. It isn’t a lack of intelligence, but crucial skill gaps that dent confidence, stall careers, and leave freshers struggling to earn basic site respect.
In this guide, for students, fresh graduates, and early-career engineers, we’ll reveal 10 essential real-world competencies colleges gloss over—and provide concrete steps to master each. By internalizing these lessons, you’ll gain the practical know-how to thrive from day one, boost your employability, and fast-track your civil engineering journey.
Table of Contents
1. Navigating Local Building Regulations
Why It Matters
Every structure—from a simple home to a multi-story complex—must comply with municipal planning rules. Understanding zoning maps, height restrictions, Floor-Space Index (FSI), and setback requirements is non-negotiable for any real-estate or infrastructure project.
The College Gap
- Theory vs. Practice: University courses cover “urban planning fundamentals,” but seldom dig into your city’s Development Control Rules (DCR) handbook.
- Approval Process Blind-Spot: Freshers rarely learn to draft “application for building permission,” calculate plan-approval fees, or track sanction timelines.
Bridging the Divide
- DCR Handbook Deep-Dive: Obtain the latest DCR for your municipality (e.g., Mumbai DCR 2034, Delhi Master Plan) and annotate sample site plans.
- Mock Submission Exercise: Prepare a simplified site plan—with plot boundaries, North arrow, FSI calc—and simulate a digital e-submission via your state’s Urban Development portal.
- Field Visits: Attend a “town planning” counter at your local municipal corporation to observe how officers stamp, query, or reject building drawings.
2. Mastering Real Estate Compliance & Liability
Why It Matters
Since the enactment of the Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act (RERA), engineers share legal accountability for project timelines, financial transparency, and defect liability. A single oversight can trigger penalties, consumer lawsuits, or project delays.
The College Gap
- No RERA Curriculum: Indian engineering programs rarely include mandatory modules on RERA definitions (promoter vs. allottee), project registration, or prescribed disclosures.
- Contract Law Awareness: Fresh graduates have minimal familiarity with FIDIC/FIECCI clauses, payment milestones, or force-majeure language.
Bridging the Divide
- Online Law Crash Course: Platforms like NPTEL, Coursera, or your state’s Real Estate Regulatory Authority often offer free short courses on RERA compliance.
- RERA Audit Simulation: Choose an ongoing real-estate project, download its RERA registration documents, and draft a checklist of mandatory disclosures vs. observed practices.
- Legal Mentorship: Connect with a construction lawyer or in-house counsel for a 30-minute chat—ask to review a simple contract clause with you.
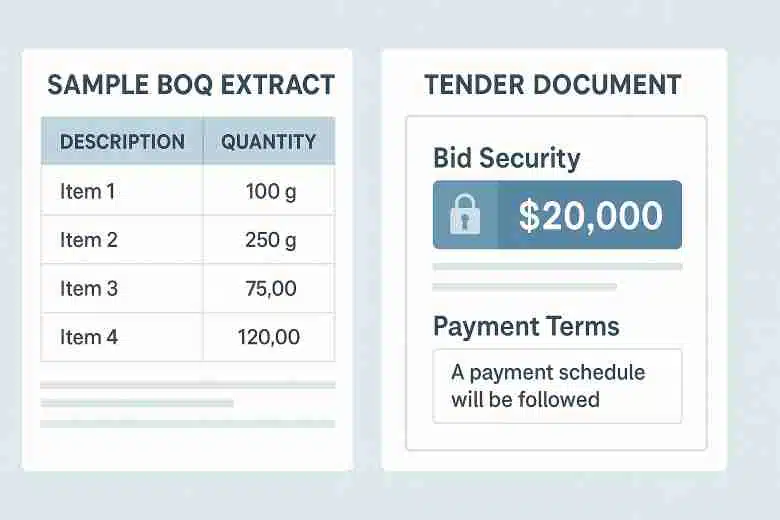
3. Quantitative Cost Management & Tendering
Why It Matters
Accurate cost estimation and proficient tender analysis separate junior engineers from experienced quantity surveyors. Employers expect freshers to prepare a Bill of Quantities (BOQ), apply correct rates, and decode commercial terms from Day One.
The College Gap
- Superficial Rate Analysis: Many courses teach “rate analysis” in principle, without live BOQ exercises or exposure to national schedule of rates (SOR).
- Zero Tender Familiarity: Freshers often never navigate an e-tender portal (e.g., eProcurement, CPPP), missing out on clauses like bid security, validity, and packaging.
Bridging the Divide
- Practical BOQ Project: Download a small building drawing, quantify items (e.g., RCC, brickwork), apply current market rates, and compile a BOQ in Excel.
- Tender Dissection Workshop: Retrieve two recent tenders (public & private) from online portals. Highlight differences in payment terms, escalation clauses, and penalty conditions.
- Peer Review: Seek feedback from a senior estimator—ask them to spot rate-application errors or missing inclusions.
4. Hands-On Site Execution Expertise
Why It Matters
Conceptual knowledge of concrete mix design won’t help when formwork fails, reinforcement isn’t properly tied, or curing is neglected. On-site execution demands a tactile understanding of construction materials, equipment, and quality checks.
The College Gap
- Limited Lab Work: University labs often test ideal specimens, not real-world variability in aggregates, water cement ratio, or curing conditions.
- One-Semester Internship: A 4-week or 8-week internship seldom exposes students to end-to-end site workflows.
Bridging the Divide
- Extended Site Attachments: Negotiate a semester-long internship—ideally with a mid-sized contractor—to rotate through concreting, shuttering, and finishing gangs.
- Skill Bootcamps: Enroll in workshops on advanced concrete technologies (e.g., self-compacting concrete, waterproofing membranes) offered by material suppliers.
- Micro-Projects: Form a campus “hands-on club” to build small footbridges or water tanks, learning bar-bending schedules (BBS) and formwork assembly first-hand.
5. Effective Communication & Project Documentation
Why It Matters
A well-written daily progress report or a clear site instruction letter can prevent misinterpretations, scope creep, and disputes. Professional emails, RFIs (Request for Information), and meeting minutes form the backbone of trust between contractors, clients, and consultants.
The College Gap
- Tech Writing Neglect: Engineering syllabi emphasize reports on “structural analysis,” not on crafting formal project memos, tender clarifications, or change-order requests.
- No Stakeholder Role-Play: Graduates have scarce practice negotiating site delays or safety compliance with subcontractors.
Bridging the Divide
- Technical Writing Short Course: Platforms like Udemy or local institutes offer modules on business communication—focus on email etiquette, report structure, and concise language.
- Template Library: Develop your own repository: daily diary formats, RFI templates, variation order sheets, site inspection checklists.
- Mock Client Meetings: Partner with peers to role-play client vs. contractor scenarios—practice delivering bad-news updates or seeking approval for additional works.
6. Strategic Career Mapping & Role Exploration
Why It Matters
Civil engineering spans diverse roles: site supervision, structural design, project management, quantity surveying, sustainability consulting, and digital-construction specialties (BIM, digital twins). Without clarity, graduates gravitate toward generic site jobs—often feeling stuck, underpaid, and unfulfilled.
The College Gap
- Minimal Career Services: Few institutes organize dedicated career fairs covering specialized roles beyond a handful of real-estate recruiters.
- Alumni Engagement Lapses: Lack of structured mentorship programs leaves students without industry guidance.
Bridging the Divide
- Professional Body Membership: Join the Indian Concrete Institute (ICI), Institute of Town Planners India (ITPI), or BIMForum chapters—attend webinars on niche disciplines.
- Mentorship Platforms: Use LinkedIn’s “Career Advice” feature or alumni portals to connect with mid-career professionals and request 15-minute informational interviews.
- Elective Upskilling: Pursue certifications in PMP (Project Management Professional), Revit BIM, Primavera P6, or sustainability (IGBC).
7. Proficiency with Software & Digital Tools
Why It Matters
The modern construction site relies on digital workflows: AutoCAD for drafting, Revit for BIM modeling, STAAD Pro for analysis, and Primavera for scheduling. Freshers who lack software fluency struggle to meet basic deliverables and lose credibility.
The College Gap
- Outdated Lab Software: Many engineering colleges still run older versions of AutoCAD or rely solely on textbook exercises instead of real-project models.
- No Integrated Projects: Students seldom work on multidisciplinary BIM projects that simulate architecture, structure, and MEP coordination.
Bridging the Divide
- Online Tutorials & Licenses: Secure student licenses for AutoCAD, Revit, and Primavera. Complete end-to-end projects from conceptual sketch to clash detection in BIM 360.
- YouTube-Driven Learning: Channels like “BIM AEC” or “Civil Engineering Academy” offer free, project-based tutorials—follow along to build sample models.
- Hackathons & Challenges: Participate in college or community hackathons where you deliver a mini-project (e.g., 3D model + schedule + cost estimate) within a time limit.
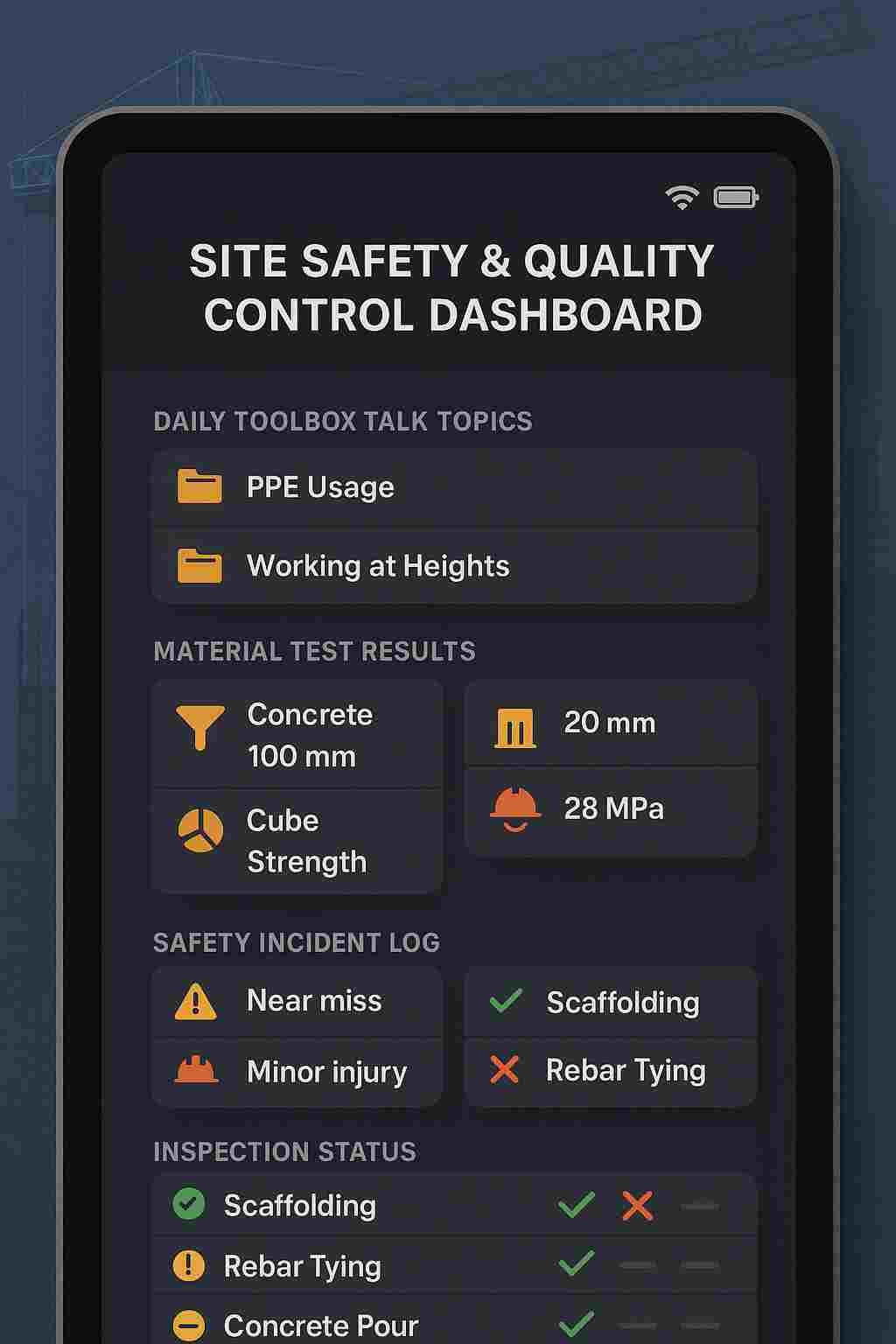
8. Rigorous Safety & Quality Control Practices
Why It Matters
Safety lapses not only endanger lives but trigger site shutdowns and liabilities. Quality control ensures durability and reduces long-term maintenance costs. Engineers must routinely perform risk assessments, toolbox talks, and material tests.
The College Gap
- Theoretical Safety Lectures: Classrooms teach IS codes (e.g., IS 456 for concrete), but rarely conduct real hazard-identification drills or mock toolbox talks.
- Limited QC Exposure: Lab tests on cubes and cylinders don’t translate directly to on-site sampling, calibration of slump cones, or sieve analysis.
Bridging the Divide
- Site Safety Workshops: Attend OSHA-approved or CISRS training programs—get certified in basic safety induction and emergency response.
- Quality Audits: Shadow the site QC engineer during material deliveries—observe sampling, test witnessing, calibration of gauges, and record-keeping.
- Daily Toolbox Talks: Lead short safety briefings for peers—even on small campus-based projects—to practice hazard communication.
9. Leadership, Teamwork & Stakeholder Management
Why It Matters
As you progress, you’ll manage tradespeople, subcontractors, and multi-disciplinary teams. Strong leadership and teamwork skills help you resolve conflicts, allocate resources, and motivate on-site crews to meet tight schedules.
The College Gap
- Solo Projects Dominance: Most assignments are individual, not team-based. When group projects exist, assessment often focuses on technical accuracy, not collaboration dynamics.
- No Conflict Resolution Training: Freshers struggle to negotiate extra hours, material shortages, or design changes with contractors.
Bridging the Divide
- Group Workshops: Volunteer to lead college fest committees or industry club events—hone delegation, planning, and follow-up skills.
- Leadership Seminars: Institutes like CII and FICCI run short leadership and soft-skills programs—attend to learn conflict management, feedback delivery, and motivation techniques.
- Peer Coaching: Foster a small study group where each member leads one weekly session on a chosen topic. Rotate roles to experience both leader and participant mindsets.
10. Adaptability & Lifelong Learning Mindset
Why It Matters
The construction industry evolves rapidly—new materials, digital platforms, sustainability mandates, and prefabrication methods emerge every year. Engineers who resist change get left behind; those who learn continuously stay in demand.
The College Gap
- Fixed Syllabus: University curricula update slowly, leaving graduates unfamiliar with cutting-edge tools like drones for site surveying or IoT-based monitoring systems.
- Limited Research Culture: Apart from a final-year project, students rarely engage in research papers or industry-academic collaborations that spur innovation.
Bridging the Divide
- Subscribe & Scan: Follow RSS feeds from journals like The Indian Concrete Journal or platforms like ResearchGate—set aside 15 minutes daily to read abstracts.
- Micro-Learning: Use apps like Degreed or Coursera’s “Skill Sets” to take 10-minute modules on emerging trends (e.g., carbon-neutral cement, robotic bricklaying).
- Innovation Challenges: Participate in events like Smart India Hackathon (Civil Track) or Builders Association innovation awards—gain exposure to real problems and propose tech-driven solutions.
Final Thoughts
A civil engineering degree builds the theoretical foundation, but true site readiness demands a broader, deeper skill set. By proactively mastering these 10 real-world competencies, you’ll:
- Earn immediate respect from supervisors and contractors
- Deliver higher-value work, boosting your career trajectory
- Mitigate risks through legal, safety, and quality control savvy
- Align your career path with emerging roles and digital trends
Next Steps for Indian Graduates & Freshers:
- Self-Assessment: Identify your top two weakest areas among the ten above.
- Action Plan: Allocate the next 60 days to targeted courses, site attachments, or mentorship sessions.
- Portfolio Building: Document each learning—upload BOQ samples, BIM screenshots, safety audit checklists—to showcase in interviews.
- Network & Iterate: Join professional groups, attend meetups, and regularly update your skill roadmap to stay ahead in India’s competitive civil engineering landscape.
Related Posts:
- Future-Proof Construction: Essential 2030 Skills
- Finding Purpose and Meaning In Life: Living for What Matters Most
- Your Complete Guide to Construction Business Management Degree
- How to Get a Job as a Recent Graduate in 2025 [Ultimate Guide]
Frequently Asked Questions
Focus on developing site execution expertise and mastering effective documentation. These foundational skills provide immediate value on-site and establish your credibility during your early career stages.
Online certifications showcase your dedication to learning but should be backed by practical experience. Working on real-world projects—like creating a BIM model or preparing a BOQ—can demonstrate your applied skills to employers.
Use your college alumni network, LinkedIn’s “Career Advice” feature, and professional associations like the Indian Concrete Institute (ICI) or Institute of Town Planners India (ITPI). When reaching out, introduce yourself clearly and specify your interest in short-term learning opportunities.
Yes, by consistently dedicating your weekends and evenings to targeted learning and site visits, you can build a solid foundation in all ten skills within 9 to 12 months.
Once equipped with these core competencies, you can explore roles such as Planning Engineer, Quantity Surveyor, BIM Coordinator, Project Manager, or Sustainability Consultant. These options extend your career path beyond traditional site supervision roles.


